by Matthew J. Klas
The importance of gas stations and convenience stores to tribes continues to be clear. The businesses include both those owned by the tribe itself and those on tribal lands owned by members of the community. Despite challenging recent years of economic uncertainty and the trials of the pandemic, gas stations and convenience stores have continued to be built and operated across tribal lands.
Approximately two-thirds of Indian tribes in the contiguous U.S. have a gas station or convenience store (c-store). Gas stations and c-stores provide goods and services to area residents, keep capital on the reservation and generate tax revenues for tribal governments. Gas stations and c-stores located near casinos can encourage guests to stay on property longer. Those with onsite gaming can have an even greater economic potential, offering a casual and convenient gaming experience to patrons.
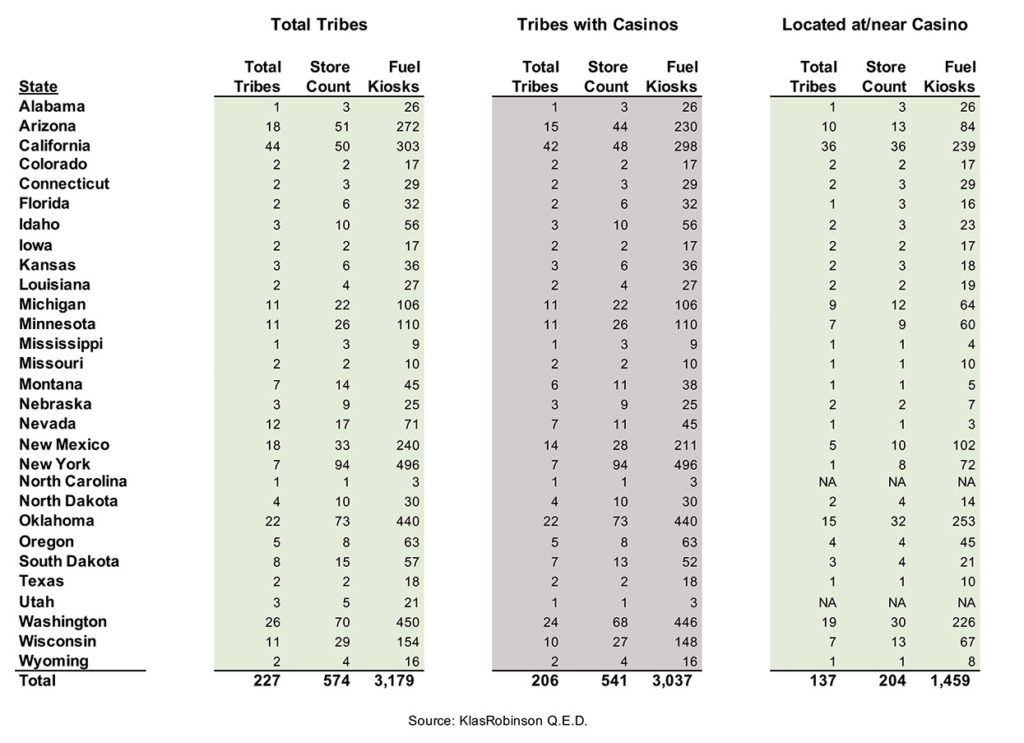
As of September 2023, there were 227 tribes with 574 tribally-owned and tribal member-owned gas stations/c-stores in 29 states. These include 206 gaming tribes with 541 gas stations/c-stores, of which 204 stores are located at or near a tribal casino. Table 1 presents a summary of tribally-owned or tribal member-owned gas stations/c-stores by state.
California has the most tribes with gas stations/c-stores (44 tribes), as well as the highest number of tribally-owned or tribal member-owned gas stations/c-stores located at or near Indian casinos with 36 stores. With respect to total store count, New York ranks first with 94 stores, many of which are small operations owned by tribal members. Oklahoma ranks second with 73 tribally-owned and tribal member-owned gas stations/c-stores, followed by Washington with 70 stores, Arizona with 51 and California with 50.
Approximately 256 tribally-owned or tribal member-owned gas stations/c-stores (44.6 percent) carry a national fuel brand. Of those with national brands, 27.3 percent are Conoco Phillips (Conoco, Phillips 66, 76), 19.1 percent are Chevron (Chevron/Texaco), 16.8 percent are Shell, 9 percent Exxon (Exxon/Mobil), and 5.5 percent Sinclair. Other national brands with more than one store include BP, Citgo, Marathon, Tesoro, Valero, Alon and Cenex.
Several tribes maintain their own fuel brands. The Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma has 17 Choctaw Travel Plaza locations, the Oneida Indian Nation of New York’s SavOn Convenience Store brand has 10 locations, the Winnebago Tribe of Nebraska, through Ho-Chunk, Inc., has six locations of the Pony Express/ Heritage brand, and the Seneca Nation of New York has five Seneca One Stop locations.
Own-branded c-stores are also found across Indian Country. In New Mexico, the Pueblo of Laguna, through its Laguna Development Corporation, has Route 66 Travel Centers and 66 Pit Stops (4 locations). In Oklahoma, the Chickasaw Nation has Chickasaw Travel Stops – CST (10 locations). In Washington State, the Confederated Tribes of the Colville Reservation has Colville Fuels (6 locations), the Puyallup Tribe has Tahoma Market and Tahoma Express (6 locations), the Nisqually Indian Tribe has Nisqually Markets (5 locations) and the Spokane Tribe of Indians has Spoko Fuels (4 locations). In Wisconsin, own-branded c-stores include the Ho-Chunk Nation’s WhiteTail Crossing brand (5 locations) and the Oneida Nation of Wisconsin’s Oneida One Stop brand (7 locations). Many own-branded c-stores still carry national fuel brands.
Table 1: Indian Country Gas Stations / Convenience Stores by State
Many gas stations/c-stores in Indian Country boast of additional facilities and amenities. Of the 574 total stores, 15.2 percent have a drive-thru smoke shop, 8.4 percent have car washes, and 12 percent have showers, laundry and/or trucker lounges. Food and beverage offerings range from basic snack food and deli-type “grab-n-go” set ups to signature roadside diners. Pizza is frequently offered. National fast-food franchises are also common. Popular franchises include Subway, Dunkin’, Sonic and Burger King.
Local communities often rely on these businesses not just for fuel, but also for food, groceries and other retail. Several tribes have developed gas stations/c-stores with expanded grocery and convenience retail, emphasizing fresh food offerings prepared on site. The Choctaw Nation in Oklahoma developed Choctaw Country Market, which features a full-service grocery store with sit-down deli area, made-to-order and pre-packaged meals, fresh produce, household necessities and an on-site butcher. To date, there are three Choctaw Country Markets in Oklahoma.
Another example is Maple Leaf Market, a convenience store brand developed by the Oneida Nation of New York, which focuses on providing healthier grab-and-go meals and made-to-order food, as well as groceries and essential items. To date, there are three locations in New York. Expanded convenience stores such as Maple Leaf Market and Choctaw Country Market can provide goods and services to local communities and generate important tribal revenue.
Gas stations and c-stores located near tribally-owned casinos can encourage guests to stay on the property longer, generating incremental gaming revenue at the casino. More than a third of tribally-owned and tribal member-owned gas stations/c-stores are located either directly at a tribal casino or within close walking distance.
Many gas stations/c-stores have gaming machines of their own. There are 107 tribally-owned gas stations/c-stores that include on-site casinos (gasinos). As presented in Table 2, these gasinos are located in 15 states with a combined total of approximately 12,500 slot machines, 20 table games and over 700 fuel kiosks. The typical tribally-owned gasino has approximately 118.4 gaming positions, 6.7 fuel kiosks and 17.8 gaming positions/fuel kiosk. However, these figures vary significantly by state. Approximately 42.1 percent of gasinos are within close walking distance of the respective tribe’s main casino. The remaining 57.9 percent are stand-alone properties.
Table 2: Indian Country Gasinos by State
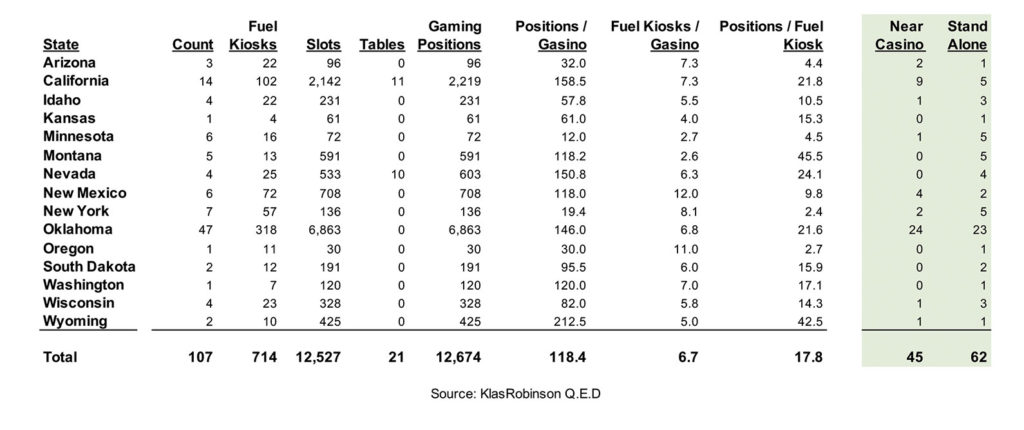
Tribes in Oklahoma have seen the most success with gasinos. The state has 43.9 percent of all gasinos, 44.5 percent of gasino fuel kiosks and 54.2 percent of gasino gaming positions in the country with 47 properties, 318 fuel kiosks and 6,863 gaming positions. At the same time, Wyoming has the highest number of gaming positions per gasino at 212.5; New Mexico has the highest number of fuel kiosks per gasino at 12; and Montana has the highest number of gaming positions per fuel kiosk at 45.5.
Indian Country gasinos tend to be physically larger than non-gaming gas stations/c-stores owned by Indian tribes or tribal members. Table 3 presents a comparison of tribally-owned and tribal member-owned gas stations/c-stores, with and without on-site gaming operations. Gasinos have a higher average number of fuel kiosks and significantly larger average building square footage due to the additional space required by the gaming operation. While gasinos represent less than 20 percent of all stores, they account for approximately a third of all gas station/c-store square footage in Indian Country.
Table 3: Indian Country Gas Station / C-Store and Gasino Comparison
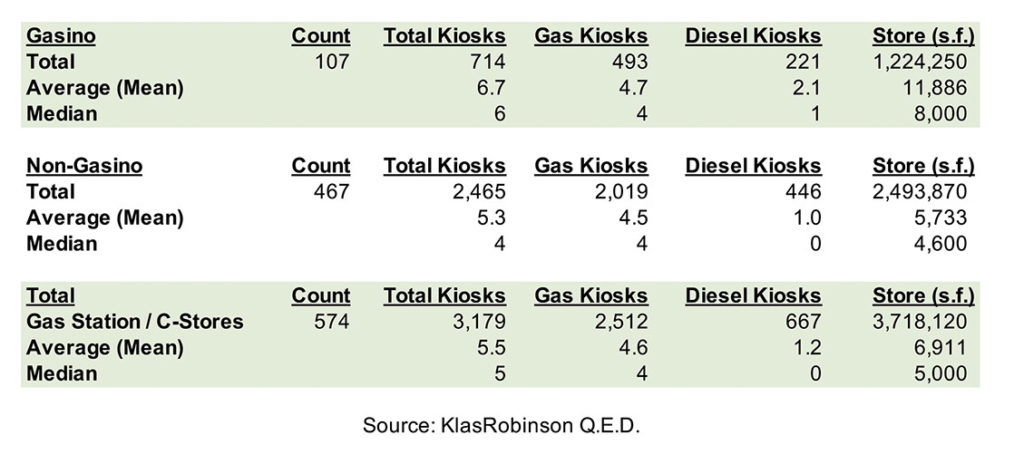
Gasinos have an average of 6.7 total fuel kiosks, 4.7 gasoline kiosks and 2.1 commercial diesel kiosks; and a median of six total fuel kiosks, four gasoline kiosks and one commercial diesel kiosk per operation. By comparison, tribally-owned and tribal member-owned gas stations/c-stores without on-site gaming operations have an average of 5.3 total fuel kiosks, 4.5 gasoline kiosks and one commercial diesel kiosk and a median of four total fuel kiosks, four gasoline kiosks and zero commercial diesel kiosks per operation.
With respect to footprint, the average size for an Indian gasino is almost 12,000 sq. ft., while the median square footage is 8,000. By comparison, non-gaming gas stations/c-stores in Indian Country have an average size of 5,733 sq. ft. and a median square footage of 4,600 per store.
An excellent resource for tribes interested in the fuel and convenience store industry is the Tribal Convenience Store Association (TCSA), which represents 57 member tribes spanning multiple states. The TCSA’s mission is: “Tribes helping tribes lead the convenience-store industry through peer networking, vendor partnerships, and member education.” Additional information on the TCSA can be found at tribalcstores.org.
Matthew J. Klas is a Senior Associate with KlasRobinson Q.E.D., a national consulting firm specializing in the feasibility and economic impact of casinos, hotels, and other related ancillary developments in Indian Country. He can be reached by calling (800) 475-8140 or email at mklas@klasrobinsonqed.com.